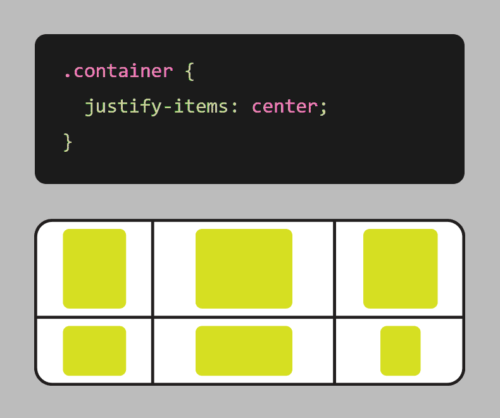
Your website’s homepage is often the first impression a visitor has of your brand, so it’s essential to make it count. A well-designed homepage can capture your visitor’s attention and guide them towards taking the desired action, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for your newsletter, or browsing your content. Here are some tips and best practices to help you create a functional and eye-catching website homepage.
- Make a plan with wireframing. Before you start designing and coding your homepage, brainstorm using wireframes and mockups to begin imagining what your final product can be.
- Start with a strong header. The header is the first thing that visitors will see, so it’s important to make a good impression. Include your logo, a headline or tagline, and a call to action. Your headline should be clear, concise, and attention-grabbing. It should give visitors a good idea of what your website is about and what they can expect to find on it.
- Create a strong visual identity. Your homepage should be visually appealing and should reflect the overall branding of your website. This means using consistent fonts, colors, and imagery throughout your homepage.
- Know your audience. Understanding your target audience is crucial when creating a homepage that resonates with them. Consider their interests, values, and pain points and design your homepage accordingly to create a good user experience.
- Keep it simple. A cluttered homepage can be overwhelming and confusing for visitors. Keep your homepage design simple, with a clear hierarchy of information that guides the visitor’s eye.
- Use eye-catching visuals. Visuals can help capture your visitor’s attention and make your brand more memorable. Use high-quality images and videos that are relevant to your brand and message.
- Keep your content organized and easy to scan. Use clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points to make your content easy to read and understand. You can also use white space to create visual breaks and make your content more visually appealing.
- Make your value proposition clear. Your homepage should communicate your unique selling proposition and what sets your brand apart from the competition. Make sure your message is prominently displayed and easy to understand.
- Make it easy to navigate. Visitors should be able to easily find the information they’re looking for on your homepage. Use a clear and concise navigation system and make sure all of your links are working properly.
- Use clear and concise copy. Your homepage copy should be simple and to-the-point. Use clear headlines and subheadings to break up the text and make it easier to scan.
- Optimize for mobile. With the majority of website traffic coming from mobile devices, it’s essential to optimize your homepage for mobile devices. Make sure your design is responsive and loads quickly on mobile devices.
- Use calls-to-action (CTAs). Your homepage should encourage visitors to take action, whether it’s signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase. Use a clear and prominent CTA to guide visitors towards the desired action.
- Optimize for search engines. Your front page is likely the page you want to rank highest in search engines. Use relevant keywords throughout your homepage content. This includes your headline, meta descriptions, and body text. Keep your homepage content fresh and up-to-date. Google loves fresh content, so make sure you’re updating your homepage regularly with new information and updates.
- Test and iterate. Once you’ve created your homepage, it’s important to test it and iterate on it based on user feedback. This will help you to create a homepage that is both functional and eye-catching.
By taking these guidelines into account, you can create a useful and enticing website homepage that captures your visitor’s attention and guides them towards taking the desired action. Hopefully this translates to closing more sales, or getting more sign-ups. Remember to keep your homepage design simple, communicate your value proposition clearly, and use calls-to-action to funnel visitors through your desired path. And always keep it up-to-date with fresh and engaging content. This will help keep visitors happy and coming back for more.