Web development is a constantly evolving field, and there are many standards and best practices to consider when creating a website. One key aspect of web development is standards compliance. This process involves ensuring that a website adheres to established standards and guidelines, such as those put forth by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Standards validation involves checking the code of a website to make sure it meets the established standards for HTML, CSS, and other web technologies. This process can be done manually, but there are also many automated tools available that can help with this task. By validating a website’s code, developers can ensure that it will work correctly across different devices and browsers, and that it is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
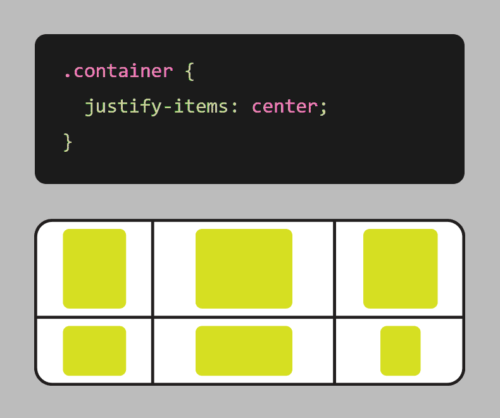
One important aspect of standards validation is ensuring that a website’s code is semantically correct. This means using HTML elements in a way that accurately describes the content they contain. For example, using <h1> tags for headings and <p> tags for paragraphs. This not only makes the code easier to read and understand, but also helps with accessibility and search engine optimization.
Another important aspect of standards validation is ensuring that a website is compatible with different browsers and devices. This can be a challenge, as different browsers and devices may interpret code differently. However, by adhering to established standards, developers can help ensure that their websites work correctly across a variety of platforms.
There are a number of benefits to validating your web pages against web standards. These benefits include:
- Improved accessibility: Ensure that your pages are accessible to all users, regardless of their device or abilities.
- Greater compatibility: Increase your website’s compatibility with all major browsers and operating systems.
- Increased performance: Validating your web pages can help to improve page load times and reduce lagginess.
- Higher search engine ranking: Search engines like Google use standards compliance as a factor in their ranking algorithm.
- Fewer errors: Greatly lower the number of errors and bugs that occur.
- Reduced development time: Reduce development time by catching errors early on. This is because standards-compliant code is typically easier to debug and maintain.
- Stronger website security: Improve the security of your website by identifying potential security vulnerabilities. Standards-compliant code is typically more secure than non-compliant code.
- Future-proof: Reduce the likelihood of your pages breaking over time.
Validate your code early and often in the development process. This will help to catch any errors early on, before they become more difficult to fix. Of course, no single validation tool is perfect. It is a good idea to use a variety of tools to get a comprehensive view of your code.
In addition to adhering to established standards, there are also best practices that developers can follow to improve the overall quality of their websites. These may include using responsive design to ensure that a website looks good on all devices, optimizing images and other media to reduce load times, and using clear and concise code that is easy to read and maintain.
By validating your code against established web standards and best practices, you can help to ensure that your sites are accessible, compatible, performant, and error-free. This can lead to a better user experience for all of your visitors.